![]()
THEME III
A DESCRIPTION OF THE WORKSHOPS AND THEIR ROLE
The role of the workshops of "Quatre-Mares"
The role attributed from 1920 to the workshops of "Quatre-Mares" is mainly the repair of the locomotives. 250 great repairs are envisaged annually. These workshops also ensure the repair of many machine components coming from the deposits and, in particular, the crews of wheels. They also make a great quantity of parts for the supply of the deposits and the shops general .
The basic difference between an establishment like “Quatre-Mares” and a deposit is in the type of interventions which they will carry out on the locomotives during their existence.
The deposits carry out visits of maintenance "in service” of the locomotives. They carry out accidental repairs sometimes when their infrastructures make it possible to carry them out. If they cannot realise them out, the locomotives are directed towards workshops such as “Quatre-Mares”.
The workshops carry out Great Repairs (GR) on the locomotives, after a course from 300000 to 400000 km, that is to say with intervals from 7 to 10 years. (a GR. counts for 10 to 15,000 work hours) and important Accidental (RA) Repairs.
The GR aim to give again at the locomotives of the performances equivalent to the new machines. Certain machines will come out from “Quatre-Mares” with an increased power, thanks to the modifications that they will undergo, following the permanent progress of railway technology.
The visit of workshops
We will visit together the various workshops at the time of the vapor and we will discover, on the way, the multiple facets of their activities whereas the production is with strongest.
During all the activity “vapor”, the Workshops of QM will be the only ones where the machines enter on a side (Paris) to exit from the other (Rouen).
They are served, outside, by a beam of ways connected at their two ends with the main railroads. Along the pinions North and South, two traversers with electric traction move. An interior transverse way is connected to the various service tracks by turntables. It transom the principal building in its medium in the direction of the width and puts in communication the various halls and workshops. The transports of parts are accomplished by overhead travelling cranes, or with accumulator electric trucks or by wagons.
To be directed, the railwaymen of "Quatre-Mares" do not refer at the cardinal points, but to the geographical location of the establishment. Thus North says “Rouen side”, the South says “Paris side”, the West says “side street” and Is “railway side”.
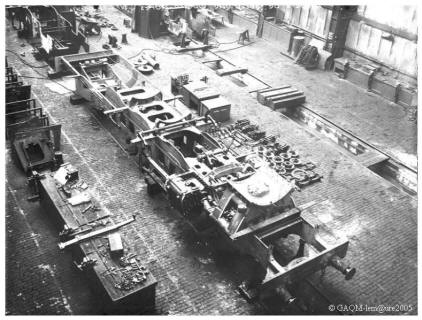
We enter the principal building by the side street and borrow the central alley which transversely cuts it by its medium. It measures approximately 250m on 105m and consists of six different halls in width and height.
The machine tool and fitter's workshop
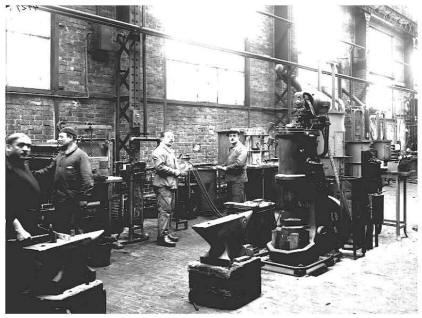
This workshop occupies the first three halls of the principal building. The first is 15 meters wide and the two others 10 meters. The first two halls are served each one by two overhead travelling cranes of 5 tons. They shelter the machine tools of average and weak powers. The teams of fitters are in charge of the repair of the parts of movement and the parts of steering gear as well as suspension, axle boxes, apparatuses of brake and valves and fittings, the workshop of clock industry and the tools.
In these halls the machine tools are joined together in group. Each group is actuated by transmissions driven by an electrical motor of 25 kw. These machine tools were not grouped by type of machines. They are placed near of fitters. Thus each team has all the machines necessary to the completion of the special work with which it is charged. In the third hall the most powerful machine tools with individual electric drive are installed. Among those we find the boring machines of cylinders, the planning machines, to slot, mill, the radial drilling machines, the vertical boring and turning lathes, etc… In this hall served by two overhead travelling cranes of 10 tons and 5 tons are also installed the teams of fitter in charge of repair of the motion rods and pistons.
The central workshop “tools”
A half-hall of the adjustment workshop is reserved for the workshop of tools upkeep. We find three teams. The first team is in charge of the repair of the pneumatic tools of half of the network. These repairs are the object of tests on bench. Each tool, drilling machine or hammer, are revised periodically. Their consumption and their power is recorded on special cards after each revision. The second team is in charge of the repair of the machine tools. Four machine tools enter in great repair each month (three for the needs for Quatre-Mares and one for the network).
This team has one turn, two grinding machines, one fast shaper, several milling machines and various test benches whose one for the measurement of the cutting pressures in turning, milling and drilling. The third and last team is in charge of the sharpening and the manufacture industry of the tools.
The heat treatment of the tools is carried out using gas ovens whose temperatures are controlled by pyrometers.
The cutting tools were standardized on all the network after the application on all the lathes of turrets “Good-Chap”. These tools are equipped with a high speed steel pastille brazed on a steel tool holder. The team must sharpen the tools of Quatre-Mares and manufacture tools for half of the network, workshops and deposits. Its production can reach a hundred and fifty tools per days.
The workshop of the "Montage"
The workshop of “Montage” occupies the two following halls and is thus situated between the fitting and the boilerworks of iron. The first hall is affected at the montage of the locomotives. he gauges 25 meters broad. It is served by two groups of overhead travelling cranes placed on two different levels. It covers three roadways on which are carried out the disassembling of the machines, the repair of the chassis, the reassembly and the finish of the locomotives.
Two overhead travelling cranes of 60 tons allow a height of lifting of 9 meters. They ensure the installation of the boilers on their chassis and can remove, by means of gantries, of the machines entirely assembled to transport them of a roadway at the other. With a height of lifting of 6 meters three overhead travelling cranes of 8 tons ensure the lifting and the fast handling of the lighter parts.
Coppersmith's workshop
The second hall, which is 20 meters wide, shelters the coppersmith's workshop (sheet-metal works and piping), the welding, the repair of the shelters, the bogies and bissels and the tenders. In this workshop are repaired the cover plates of the boilers, pipings of brake, greasing and alimentation.
its tools understand in particular a bending machine the pipes and a spot welding machine which allows the manufacturing of ashtrays. grids at sparks, couvre-roues, shelters and, in general, all parts makes with sheets of maximum thickness of 5 millimetres .
The welding
The section “welding” occupies about fifty agents. Forty works on fixed job, either in oxyacetylene welding, or in arc cutting.
The oxyacetylene welding will be equipped in 1935 with a power station of production of acetylene with high pressure and distribution with oxygen. Acetylene is produced by a battery of 3 generators with carbide. These generators are protected by a battery of hydro valves preventing any return coming from the drain of distribution. This installation is completed by an auxiliary attachment of washing and gas cleaning. The unit is controlled by a central station of adjustment. Oxygen is provided by a battery of 60 bottles of oxygen (7m3 under pressure) assembled on an automobile trailer.
Each day, the supplier changes the trailer and invoice with the workshops only gas the exact consumption of the day, by reading of the differences in pressure on arrival and departure. Two fixed batteries of succor comprise each one 12 bottles of 7 m3. The distribution of oxygen in the workshop is ensured by 121 stations which are distributed in the various sections and allow interventions in any point of the establishment.
The electric welding is under development perpetual. The applications of the arc cutting become each day more and more important. This kind of welding also experienced a notable development over the years.
The installation of an electric power station of welding to D.C. current, whose generator of the type “Compound” outputs up to 1000 amps and brings a tension ranging between 45 and 60 volts, feeds 7 stations. These stations are equipped with resistances of adjustment allowing a variation from 50 to 250 amps. The workshop of “montage” also has a spot welding machine of a power of 180 kVA allowing the welding of two 8 mm thickness sheets.
The six best welders of "Quatre-Mares" are specialized with delicate work on steel and copper. They carry out, in the workshops and in the deposits, the weldings top of tubular plate of hearth, the replacement of tube banks, the manufacturing of welded hearths, the replacement of pieces of box at fire and more especially particularly delicate work like the repair of fissured or smashed cylinders. This section develops besides constantly, the applications of the welding becoming each day more and more important.
The repair of the shelters, bogies and bissels
Nothing of notable in this section except a shear able to cut out on an unspecified profile of sheet being able to reach a 8 mm thickness.
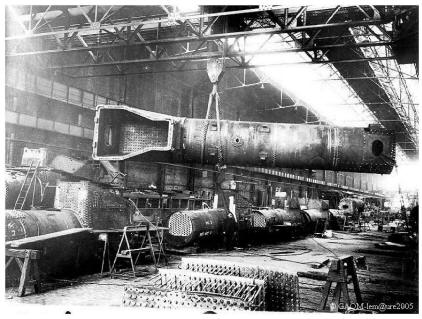
The Boilers workshop
The workshop "Boilers" occupies the last hall of the principal building. It is isolated of the other workshops by a brick partition on the entire length of the building. “Paris side” is used for repair of the boilers, as other half, “Rouen side”, is used for the forming of the substitution composants .
He measuring 25 meters wide. This workshop has two 40-ton cranes, two 10 ton and one 5 ton. The "Machine tools" and forges are installed side Rouen. They are served by overhead cranes from 5 to 10 tons that move along the length of the workshop. The bridges of 40 tonnes are placed at a higher level and serve only half of the workshop, side "Paris", for handling boilers to be repaired.
At the side "Paris", a bridge of 25 tons, moving at a great height on the railroad, can manoeuver a hydraulic rivet press. This workshop includes, among others, four radial drilling machines for the drilling's of the tubes plaque and the perimeter of the "firebox", two Plate-bending rolls, a bending machine profiles and a site drawing with a hydraulic accumulator and a 250 ton press for forming elements of steel firebox (front and rear), and finally, a "work site" for testing the "tanks-air" of the locomotives, at the air and at the water . It is also noted in the boilerwork, an apparatus for x-ray welds elements of boilers (fire steel trap "Nicholson", etc. ..). This unit with a capacity of 250 KVA allows the penetration of a plate 20 mm thick, with an installation of 20 seconds, and make sure to touch up any.
The workshop "forges" and repair of flues
The workshop "forges", built in 1923 in a building south of the previous measures 25 meters by 250. It is served by an overhead crane of 8 tons. It includes the forges themselves and the repair yard of the tubes. Contrary to what one might expect a priori, despite the importance of welding and cutting, the volume of work forges run workshops Four-Mares is important. Blacksmiths have hammers at various engine powers ranging from 350 kg to 2.5 tonnes, and a masher matrix and a forging machine.
The repair of flues, which occupies part of the workshop consists of two chains for the splicing pipe by electric welding in combination; one for smooth tubes, one for superheater tubes. The chain of smooth tubes is formed by sloping trestles served by elevators at air that bring by groups, the tubes at each workstation. Thus equipped, this chain is capable of sustained production of four hundred tubes per day and serves the needs of the entire network. The chain of superheater tubes works in a similar way, but the swaging is at cold
Outside the workshop is situated a work site of cleaning of the tubes. It consists of four machines to descale commonly called "Trommels", a work site with two saws for cutting to length, and one see-saw automatic for removing the tubes too light (ie arrived to wear limit), a tank to clean tubes, pipes repaired and new. The loading and unloading of cars as well as the stock is provided by a 2-ton gantry bridge with electric drive
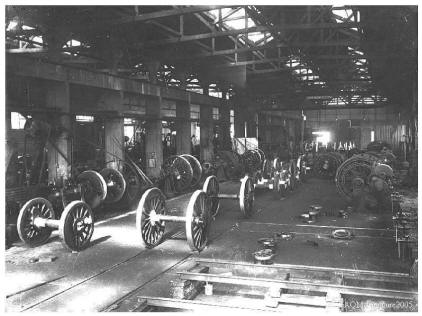
The workshop on wheels
This workshop located on the other side of the main building, in the north court measures 90 meters by 34 m, 50. It has two halls that are served by four bridge of 8 tons. The raceways are extended outside the workshop, for the wheel park service . Two movable flaps can give passage to the bridge and then close the sprocket of the workshop on the wheels park side. One of the halls includes the lathes for refresh the bandages of wheels, including a lathe "HEGENSCHEIDT" and the lathes for rectify for swivel pin
The other hall shelters the vertical lathes for bored the wheels bandages, with a tower 2.10 m bore capacity, making six bandages in eight hours, the mazout oven to heat the bandages, the machine to crimp the staples by percussion, and finally the press to shimming and the few machines (lathes, planers, drills) needed for the preparation of axles and wheels. With tolerances of manufacture by 0.2 mm, this workshop, in a service 2 / 8, rehabilitates one hundred and fifty axles per month.
The secondary buildings
The workshop of heat treatment
The carburizing and the tempering are operations which aim at bringing to the steel a superior hardness. They are realized on all the parts bound to the safety such as piston rods, connecting rods etc. and are made in a special building. This last one, built in reinforced concrete, is 16 meters on 10. The equipment of this workshop contains an oven in cémenter, an oven with bath of salt, an oven with mitten, warmed in the mineral oil, and the tubs necessary for the tempering. Adjacent to this workshop, is situated the workshops of régulage and sanding as well as the post of fire fighting endowed, among others, with a motor-pump LAFLY.La bouillotterie
The bouillotterie is installed in a building in reinforced concrete being 15 meters on 25 and served by a 3 ton overhead crane. This last one is used for the cleaning of the parts of locomotives. Those this are placed in tubs with potassium hydroxide covered with range hoods connected with a driving of aspiration for the evacuation of vapors. the cuves are warmed by means of serpentines of vapor fed, in winter, by the boilers which are of use to the heating of workshops and, in summer, by two boilers of locomotives installed in the building.
The substation of electric transformation and production of air.
This building, of 25 meters on 8, shelters four converters of 100 kW for transforming the three-phase current into direct current. The electrical energy is supplied to the workshops of Quatre-Mares in the form of alternating current in 5 000 V; her tension is returned to 220 V in two posts and in a substation, a part of the current is transformed into direct current.
She understands, furthermore, vertical compressors which produce the air distributed to the various workshops by a pipeline network. In the part of the boilermaking of the multiple air inlets are installed at feet of every column as well as in pits established under the central way of the workshop for the repair of boilers.
The painting workshop
The painting of locomotives is made in a workshop, also in reinforced concrete, of 36 meters on 16 and provided with an air source special heating. This building will be use little to the painting of locomotives. He will be transformed, in 1932, into training school.
The installation for the weighing of locomotives
The weighing of locomotives is made by means of seesaws installed in a special building containing eight couples of seesaws of 12 tons on wagons moving in a pit 18 meters in length. The weighing allowing to distribute fairly weight of the locomotive on axles.
Additional buildings
The store of workshop
This store covers a surface of 1000 m2 and stores the matters necessary to the needs for the workshops. It is equipped with a goods lift . A small building site of cutting understands alternative saws and a saw “Heller”, for rendering possible to deliver to the workshops only the lengths bars or sections strictly necessary.
Offices of the administration
Installed in a building built with the main entrance of the workshops, they comprise besides the offices, the buildings of the medical department which includes a waiting room, a room of consultation and a room of bandage. A second building, close to the precedent, shelters the office of organization of work as well as a refectory in which 70 agents can take their meal.
One will notice on these 2 buildings, the presence of clock.
The cloakrooms and washbasins
Cloakrooms and washbasins are installed in lean-to building of 4 meters width built along the longitudinal frontages of the various workshops and a little below the level of the ground, so as not reduce the surface of glass lighting laterally the workshops. The water of the washbasins is heated in winter.
The heating of the workshops
The vapor necessary to the heating is produced by two boilers “Babcock” of 235 square meters heating surface, installed in the workshop of the forgings.
The vapor, under pressure and overheated, is distributed in the halls of the principal building and the workshop of the wheels by means of overhead conducts, on which the radiators are connected.
Consisting a series of twelve horizontal steel tubes 60 mms in diameter welded with each one of their ends with two vertical tubes of 120 mm.
An automatic drainer, placed at the lower part of each radiator, makes it possible to evacuate condensate in a return line to the boilers. This overhead conduct is placed beside the conduit of vapor.
The system of heating, very simple and few cumbersome, is very effective. he allows, in the workshops, to augment the temperature with 15° above the outside temperature.
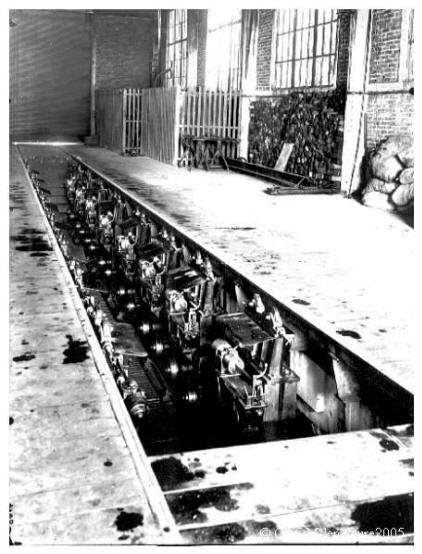
The coating of the soil
Except in some parts, in particular in the vicinity of forges, the coating of the soil in the workshops is consisted a wood paving posed on a cement finish; this in order to preserve the state of the parts in the event of fall of the one of them, or quite simply for their storage with the very soil
Here you can see the floor covered with wood.
© GAQM2016 joel.lemaure@outlook.fr