![]()
THEME IV
THE OVERHAUL OF STEAM LOCOMOTIVES
(from 1920 to 1938)
THE STEAM LOCOMOTIVES
In order to situate the principal components of the locomotives repaired in the workshops of QM, here is, in some lines, a talk on the general information met on the steam locomotives.
The principle of operation of all the steam engines is the same one since the origin. First of all, the coal, which burns in the hearth, heats the water contained in a boiler, thus producing vapor. This one impels with a piston a back and forth pass. The reciprocating motion of this piston is transformed into rotary movement via a crank-connecting rod system.
DESCRIPTION OF AN STEAM LOCOMOTIVE
The chassis
The chassis is composed of two girders firmly braced which make it indeformable in spite of the considerable efforts to which it is subjected.
These girders are made up:
- by sheet steels rolled, of which the thickness is of approximately 40 mm.
- by cast steel bars, which can have a thickness going up to 140 mm.
The châssis rests on axles. The driving wheels of the locomotives at high speed have a diameter understood between 1.80 m and 2.10 Mr. Celui of the machines intended for the trailer of the goods trains is located between 1.20 m and 1.50 Mr.
What characterises mainly an locomotive, it is its adherent weight, whose immediately has a rather precise idea by the number of the coupled axles.
It is this number which the S.N.C.F will choose in 1938 to characterize the type of locomotives, taking example on the system of classification adopted in 1925 by the Paris-Lyon-Mediterranean rail network.
We shall make him precede by a figure to indicate the number of the axles which precede the coupled axles (one 1 to indicate a bissel and one 2 for a bogie) and we shall make him follow by a figure to indicate the number of the carrier axles which follow the coupled axles. This numbering is a real index card of identity. She indeed supplies invaluable indications on the characteristics of locomotives.
The usage to indicate a type of locomotive by a single name as "Pacific", "Jackstraws" or still "Mountain" comes to us the United States. It is the classification of Whyte universally known.
The boiler
The boiler is of type tubulaire and contain tubes with smoke. The water is contained in a cylindrical body crossed, on all its length, by a beam of parallel tubes of steel, the number of which can be about 200, adjusted in both funds of the cylindrical body.
The foyer of the locomotive underwent diverse improvements during the years, to decrease the fatigue of the staff of conduct. Certain locomotives with fire chamber in the coal received a device of mechanical load, the "stoker", which avoids the load at the shovel. some locomotives were endowed with a foyer warmed in the fuel oil.
Two phenomena always worried the engineers. They are the entartrement and the corrosion. The scale deposit is fatal in the good heat transfer and decreases the return on the boiler. As for the corrosion, she exercises a destructive influence on the sheet steels of boilers.
A process, effective to fight the entartrement and the corrosion, is imagined by Mr. Louis Armand. It is the "T.I.A" (" Complete Treatment Armand "). This process, based on chemical reactions, will decrease the maintenance costs and will increase times between periodic operations. Besides, he will lower the consumption of fuel from 65 to 52,4 kg for 1000 tons-kilometers dragged
We shall add it a complex " antifoam " for avoid in locomotives the phenomenon of "braking". That is the training of the water of the boiler by the escape. What could entail, by wash of cylinders, their deterioration at the same time as a decline of power.
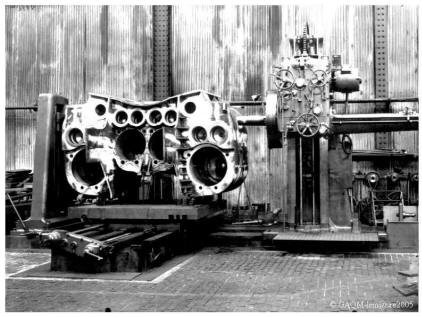
The engine
The vapor taken in the top of the boiler, in what is called the dome of vapor, is brought in a cylinder where moves a piston.
The engine of the locomotive contains the other numerous more or less complex organs. Among these, we shall quote the system of distribution.
The vapor must be managed sometimes on a face of piston, sometimes on the other one. There are several types. We shall limit to quote one of the most wide-spread which is the system " Walschaerts ". In that case the organ which adjusts the admission of the vapor in the cylinder and its escape can be a cylindrical drawer, a set of valves, etc... The distribution " Lentz " goes into this last category.
On locomotives called " to simple expansion ", the vapor works in two cylinders where it is admitted at the pressure of the boiler. Then, she escapes then directly in the chimney. Other locomotives, very wide-spread in France, are called " in double expansion " or " compound ". In that case, the vapor having worked in first two cylinders, called "at high pressure", relaxs only partially, then is sent to two other cylinders called "low-pressure", where from it escapes then by the chimney.
The repairs realized on steam locomotives.
Since their date of manufacture until that of their reform, locomotives and the tenders is carefully followed. They undergo systematic revisions according to their mileage and to their general state.
To assure in the best economic conditions, the maintenance of the park of locomotives, is established a program of repair based on the real state of machines and possibilities of supply. This one is established on March 31st for the next year and is biannually adjusted.
It is the deposits which supply the elements of this program, by taking into account the average mileage and the state of foyers. For every locomotive a descriptive state of boilers is held up to date by the warehouse. It is added to the file of the locomotive.
Locomotives are sent to the big workshops of rail networks, such as that of "Quatre-Mares", or the Private industry (LCB Nantes for the rail Network the West - Schneider in Caen where the costs of the repairs are in 1920 three times cheaper than to Sotteville), either for the big repairs ( GR) or for the accidental repairs of the frame and the mechanism ( RA) or the boiler ( RAC) or still with lifting ( RAL).
The deadline between 2 "GR" varies, following the type of locomotive, from 200.000 to 540.000 kilometers. What represents a service from 6 to 10 years. The main works realized during these "GR" concern all the deposited pieces, evaluated, repaired, or replaced to obtain a machine to the state of new.
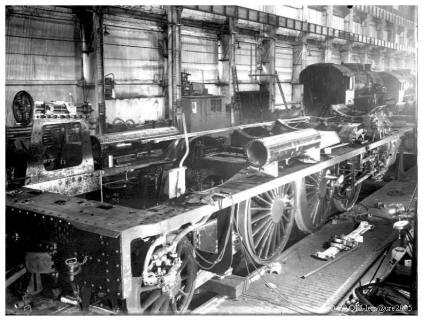
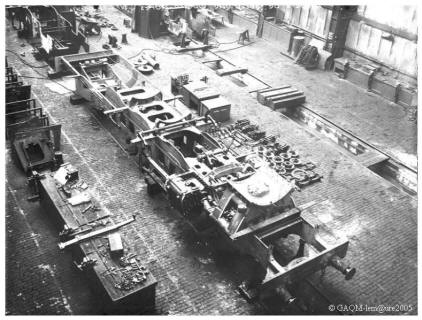
The disassembly of locomotives.
Here are now, the various operations realized on a locomotive, since its entrance until its exit, forty days later, workshops of "Quatre-Mares".
From its entrance in the hall of "assembly" by the side "Paris", the machine, delivered to a team of démonteurs, is completely undressed in three days.
Some call this operation: " La désaille ". Machines are disassembled near the building of washing, side "Paris". The parts of detail are transported in full of holes tubs, which are directly plunged into tanks of degreasing.
After cleaning and after pricking at jackhammer, the frame is moved by means of bridge of 60 ton , on a place free of the site of repair of chassis.
The Hundreds of parts which compose the chassis are distributed. Then at once between the specialised teams, in the various workshops, the work progresses at the same time in all the points of the workshop, supervised by the service of the central regulation, the real brain of the set.
The boiler, the wheels, the parts of movements, the suspensions, the faucet factory, etc. are repaired in the secondary workshops by specialised teams.
The repair of the chassis.
Since its implementation on its post, in the hall of "Assembly", and during all the duration of its reconditioning, the chassis stays at the same place where specialised teams succeed one another.
The "downright" (operation intended to control the geometry of the chassis), corrected sometimes by interventions of boilermaking, is controlled by a team endowed with eyeglasses optical and with measuring instruments " Zeiss ".
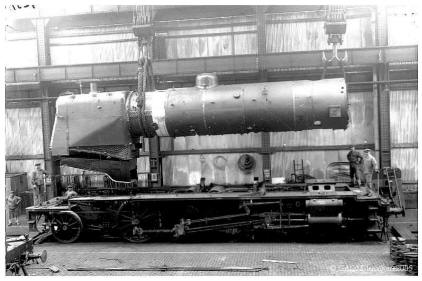
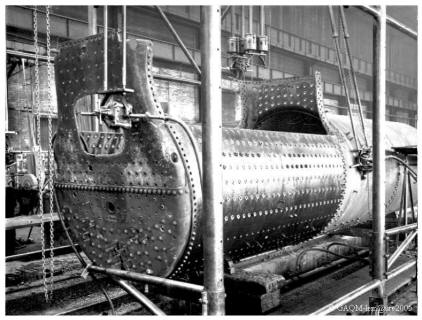
The repair of the boiler.
Forwarded on a wagon since the workshop of "Montage", the boiler follows in the hall of the "Boilermaking" a progress parallel to that of the chassis.
After the removal of tubes and the descaling with the pneumatic pneumatic drills, it is proceeded to an expertise determining the parts of the foyer to replace.
After the disassembly of the elements of the foyer, on cradles for facilitate the rotation of boilers, these last ones are brought by means of overhead crane on the places reserved for the specialized teams. A second fixed expertise, then definitively, in the detail, all the works to be executed.
The presentation and installation of replacement parts, and various repairs are undertaken. From the presentation of the foyer in the firebox, the boiler is engaged in a series of portico, under which she is presented by moving the frame in the air, put on "Lorry".
We meet successively, by following this chain of ending, press them to rivet frames, portico of tapping and pose of spacers, portico of riveting of spacers and finally the post of implementation of tubes and assembly of the faucets.
Having undergone the hot hydraulic tests under the watchful eye of the mining engineer of the APAVE, the boiler returns to the "montage" where it is put back in place in position on its chassis.
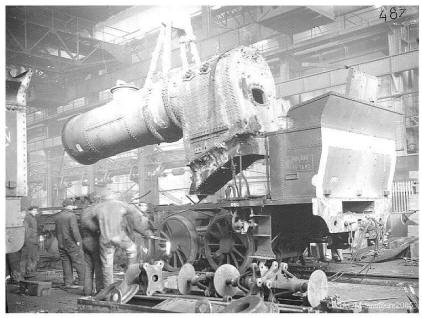
The reassembly of locomotives.
All other parts also return, and in due course, are gone back up by the specialized teams. After presentation of the boiler, on its frame put by level, the restoration of the chassis ends by the reassembly of connecting rods, the regulation of the distribution, the assembly of the pipings of the brake.
The equipment of the boiler continues with the reassembly of sheets of envelopes, valves and fittings, piping of greasing, sand pits… Once equipped, the frame is descended on its wheels in the other part of the workshop, i.e. at the end Rouen side.
The set up of the shelter and the linked pipings, the ended machine is put in pressure, weighed, and, after essay of the waterproofness of all the pipings, is presented to the agent desk clerk of the rail network.
This one verifies the locomotive contradictorily with the department head of the control of workshops and made do an on-line essay of 30 kilometers.
After painting, machines are delivered to the deposits, except the machines of speed which make a new route of guarantee from 500 to 1000 kilometers supervised by the agent desk clerk of rail network, before getting back their warehouse.
WORK ORGANIZATION
Here's how are organized before the Second World War, the distribution, execution and control of work.
The framework of "Mares Four" consists of three main services in constant contact with the workshops of executions.
The service implementation is responsible for the preparation of the work and of expertise to perform the work, translated into order of labor and material.
The control center that coordinates the execution of the work in the workshops and to ensure they are executed according to an implementation plan prepared in advance.
The technical service, independent of production, constantly seeking to improve production by improving the tools and methods.
Besides these three main services are placed three ancillary services.
The Control service is responsible for verification and validation of the work delivered by the workshops.
The accounting department that calculates the cost of the work delivered and present the monthly workshops.
The administrative department which deals with personnel matters, attachments, permits, appointments ...
The service "implementation".
The service "implementation" consists of two separate offices, one responsible for the preparation of the work in terms of labor, and other terms of supply.
After disassembly of a locomotive, the removed parts are immediately distributed among the teams. Each is then reviewed by the specialist staff of the service who deduct their deformation and wear and repairs to make. They are annotated on a "book expert". Parts can also be replaced. In this case, the "nomenclature books" are to be established..
These documents are put handed to the typists. They allow the fast establishment of the vouchers of works and the vouchers of materials. The first ones indicate to the workers the nature of the works to be executed and the necessary weather to realize them, while the second are sent to the store of workshop.
The vouchers of workforce are transmitted at the " central regulation ", for the follow-up of the board of production. They are registered by the expert on specific sheets to every team specialized of the workshops.
The vouchers of materials are sent to the store which delivers to sections the commanded materials and them made tidy up in adequate lockers.
By comparison between the emitted vouchers and the vouchers of reception, the service of implementation knows daily the late deliveries and quickly intervenes with the store.
This service establishes then, with its price lists, estimate asked by the service of the " central regulation ". He controls the invoices of the works executed for external services, distributes and classifies drawings necessary for workshops.
The central regulation.
Driving center of the workshops, this service receives all the vouchers emitted by the service of the "implementation" and distributes them immediately for execution between the heads of the interested divisional workshops. He watches the execution of the works, non-stop nor jolts, by means of graphs " Gantt " of progress (standard by series of machines) which give him all the time the state of progress of all the current works. The update of these is made during a daily conference which gathers all the foremen. The central regulator arranges all the means of the workshop to avoid in jolts or to straighten a situation compromised by an unforeseen incident.
For every locomotive in repair, a graph presents, by detailed operation, the planned and compulsory walking.The "real" walking, pointed in red every day, has to overlap in the "planned" walking. A delay on an operation which can have grave repercussions on the other operations relative to the same locomotive or even on those other locomotives.
Jointly at the repair of locomotives, workshops execute repair works of diverse parts for the deposits and make new parts for workshops shops .
The central regulator is informed on the capacities of the workshop in each job by means of a charging panel which indicates the monthly number of hours that can to provide the categorys of machine tools, the number of hours represented by the works in progress, and the number of hours necessary for the orders on standby.
It can thus quickly see the relationship between the requests and the possibilities for execution. By comparing the number of work hours available monthly in each team and the number of hours represented by work already ordered. It accepts or refuses the additional orders which are proposed to him.
These commands are not the object of individual graphs. The central regulator determines the dates of finish for every workshop and the final delivery date. He establishes the vouchers of workforce, the vouchers of materials and a sheet of routing prescribing the succession of the works in the various interested workshops.
It controls the completion of work and the delivery, thanks to a double bill book (by delivery date and customer). The divisional foreman distributes the vouchers of labor to his foremen, section head, which then gives them to the foremen, according to a charging panel adapted, for execution or classification on standby in the boards of planning of team.
Engineering service.
It is charged to improve quality of delivered work and the output ofthe workshops, by studying with the greatest care, the detail of each operation. It determines, in each particular case, the work method or of the most advantageous machining. Its agents, selected among best, are grouped in the following specialized teams:
Inspectors of machine tools
They periodically visit the machine tools of which they draw up, at the time of their first examination, the complete dossier
This file understands a “file of the characteristics” of the machine and a “inventory list” of its state at the time of the inspection. The repairs necessary there will be defined.
The Demonstrators
These selected professional agents carry out after study the first series of parts. They proceed then to the clarification of the recommended methods, the tools and montages created to realise them out.
After the examination of a proposal for a amortisation of material to be acquired, and its acceptance by the chief of the workshops of "Quatre-Mares", the study is transcribed on a “instruction document”. The latter reports the quantified conditions whereby work must be carried out (speed, advances, depth of cut). This document is given to the blue-collar worker at the same time as his work sheet and the tools for special montages necessary at the execution.
The Draftsmen
They are in charge of the production of the drawings of tools and the studies of standardization of parts, trained by the phased introduction of standards and at the work on measure in machining. Finally a special service is instructed, at the request of the "central regulation", to carry out as scientifically as possible the various tests of tools and others. he presents the results in the form of graphs, avoiding any controversy with the suppliers.
The Control service.
Certain phases of the repair of the locomotives are checked by the control service, such as the presentation of boiler on chassis and the setting on wheels. This service controls, prior to delivery to the workshop of the montage or the warehouse, the parts repaired in the various specialized workshops (limp, rods, etc) and carries out some checks by survey of the intermediate operations.
After the revision of the machine, it carries out a front control, during and after the tests "cour" and test "line". This in order to announce to the interested sections the final improvements to be carried out before the contradictory examination for the final acceptance (V.P.P) with the service "Traction"
The Accounts Department,
This service prepares pays it of staff according to the monthly attachments of the agents held by the team leaders and controlled by the administrative service of the workshops. A device of bonus is established for the agents according to the respect of time contracts.
The service determines also the cost price of the work delivered by the workshops by adding the expenses of labor and the amount with the matters consumed for this work.
Lastly, it establishes the monthly accounting balance sheet of the workshops, by comparing the statement of the real expenditure and the amount of the invoices of the month with the budget allocated with the workshops.
The Administrative service
This "service" controls the attachments of staff held by the team leaders with the pointing. It has the load of the establishment and the distribution of the licenses of circulation, of the vouchers of medical visit. Moreover it records and classifies the correspondence of the services and the workshops.
THE MODIFICATIONS CARRIED OUT ON THE LOCOMOTIVES
The “west network” is characterized, at the beginning of the century, by its lack of locomotives of large and average powers.
In 1909, the new network of the State orders 50 “Pacific” (future 231-011 to 060). The startup in 1910 of Pacific “State” 6511 to 6530 (231B) then 231.11 to 60 fact following the increase in loads. They result from the prototypes (2901 and 2902) of the network of the West. These last, exits right before the repurchase of the network by the State, are however not at the point.
la "Pacific" 2901 du réseau de l'Ouest
At that time, in the urgency, one builds new locomotives of the type already exceeded like the 230.
The use of bogies on the towed material, and consequently the increase in loads, encourages the network to command in 1913 news “Pacific”, "compound" and with overheated vapor, the 231,500.
The deliveries will spread out until 1923, delayed because of the events of 1914-1918.
In 1927, the power of the “Pacific” appears insufficient. The arrival of the metal cars complicates the situation. These problems of power lead the network of the State to undertake speed test(140/150 km/h). Following these tests, 10 “Mountain” of type “East” are adopted by the network in 1930. Another ordering of 29 similar machines follows in 1931.
With the analysis of the results of the tests of these last locomotives, in 1932, and while following the prerogatives of Mr. RENAUD who has transformed the "231,523" in machine with 3 cylinders, the service of the Material of the network of the State carries out a study of “Mountain” with 3 cylinders, simple expansion and distribution RENAUD.
This machine, "241,101", in service in 1933, does not satisfy the network with the State. It is quickly parked before being taken again by Mr. CHAPELON who in fact an excellent machine, the 242 A 1.
la 242 A 1
At that time the park of the locomotives of the network is subject only to modifications.
Half of the number of the "Pacific" are transformed at the workshops of "Quatre-Mares". Transformations are carried out on a few Mikados without to be applied to all the series.
Modifications will be also made to the level of the tubular bundel, of limps with fire, of the cylindrical body and the engine. Moreover, during their career they receive an exhaust “Kylchap” and avoids smoked.
Leur service comporte des express, des rapides et des messageries.
In 1933 the workshops transform six 231-500 into 231-500 D.
The modifications relate to:
- the installation of 28 superheaters elements "Houlet" with tubes of return 31.38,
- a regulator of great sections,
- new conduits of admission,
- one distribution at "BP" by valves with oscillating cams Dabeg ordered by Walschaërts mechanism,
- an exhaust “Kylchap” 1 K/T,
- one limps at lengthened smoke, the column of exhaust becoming rectilinear,
153 machines will be thus modified with the workshops of QM
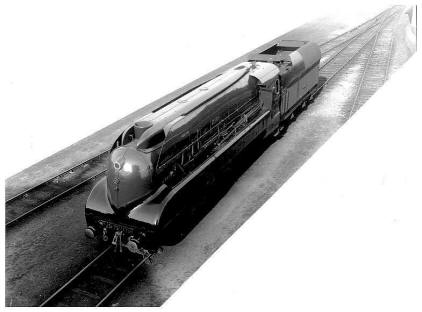
la 231.761 carénée
It should be noted that the 231,761 receives an aerodynamic careenage which will be dismounted later on. 22 machines will be transformed into 231-500 W and will become 231 F.
The 1st to leave Sotteville Q.M, in July 1933, is the 231,736 W . the operations carried out on these machines are the same ones as on 231 D, except the engine, whose BP cylinders are provided with distributers “Willoteaux” with double admission and double exhaust.
On the level of their power, it is identical to the 231 D.In July 1935 came out the DD 231 644. This is the first machine converted into 231,500 231 G according to the principles applied to the 3566 of the P.O. The transformations of the boiler are the same as those performed on the 231 D or 231 F.
The main innovation lies in the 4-cylinders whose distribution is of type "Lentz Dabeg" oscillating cam. Several test series highlight their significant gain in power, and lower in large proportions, their consumption of coal and water.
The 250 machines of series 141,001 to 250, which will become the 141C receive feed water heaters and exhausts “Kylchap” 1K/T.
The 141.050 is transformed by Mr. RENAUD during his passage to the workshops of Q.M in 1928. She is equipped with 4 valves by cylinder. The modifications which are brought concern especially the distribution, of the same type as that was adapted on the 030.729, 16 years previously. She consisted of a mechanism of distribution by valves with independent phases.
This time Mr. RENAUD, chief engineer of workshops, can have an overheated steam engine. The essays show a light decrease of the consumption but are classified without continuation because the economy does not seem sufficient in the time.
la 141.136
The 141.136 transformed at Quatre-Mares in 1938 receives a distribution " Dabeg " with cam rotary press. His stamp passes to 14 HPZ and a heater " ACFI " is installed. The results of the essays to whom she is subjected were regrettably never communicated. Of more this machine will be destroyed in a bombardment after its passage in workshops.
The 141.113 (141 C 113 - 141 E 113) is modified to Sotteville Quatre-Mares during his coming in GR in 1944/45. His surchauffeurs elements are replaced. The objective is to increase and to optimize the sections of passage of the vapor. She is tried on-line as well as in the bench test of Vitry. We notice then an increase of the power and a decrease of the consumption. 30 locomotives would have of then to be so modified if the reception of material new had not made them obsolete.
THE BIRTH OF THE S.N.C.F.
If the nationalization of railroads is in mind of the government of "Popular Front" elected in May, 1936, it is that under the government of the radical " Chautemp " that the decisive step is crossed.
The S.N.C.F is created by the law of August 31st, 1937, but the statuses given birth in the pain are put deposited on December 31st, 1937.
The S.N.C.F. takes care the whole French network on January 1st, 1938. At this date the workshops of Quatre-Mares which assure all month 7 or 8 GR ( Big repairs), 3 or 4 RA ( Accidental Repairs) and the preparation of numerous parts for the deposits, are endowed of important one and relatively modern workshop of mechanics.
The workshops of QM are attached to the district of Sotteville. It forms a coherent whole of establishment. He include the workshops of Quatre-Mares, the workshops of cars and wagons of Sotteville Buddicom, of Mézidon, service of small talk, the service electrical Sotteville and school learning of QM.
But this nationalization is going to impose new rules of the game. The new boss who is the State inherits responsibilities of the managements of the former companies.
He became manager of an industrial public service who employment about 500.000 agents and in the structurally overdrawn functioning. The limitation of this deficit is going to become the priority of the State. He is going to take care of it with more or less of success, but with more severity than the managements of the former companies.
© GAQM2016 joel.lemaure@outlook.fr